All about tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)

Article written by

April AcernoContent Writer
Content reviewed by

Chris Wood PharmDMedical Reviewer
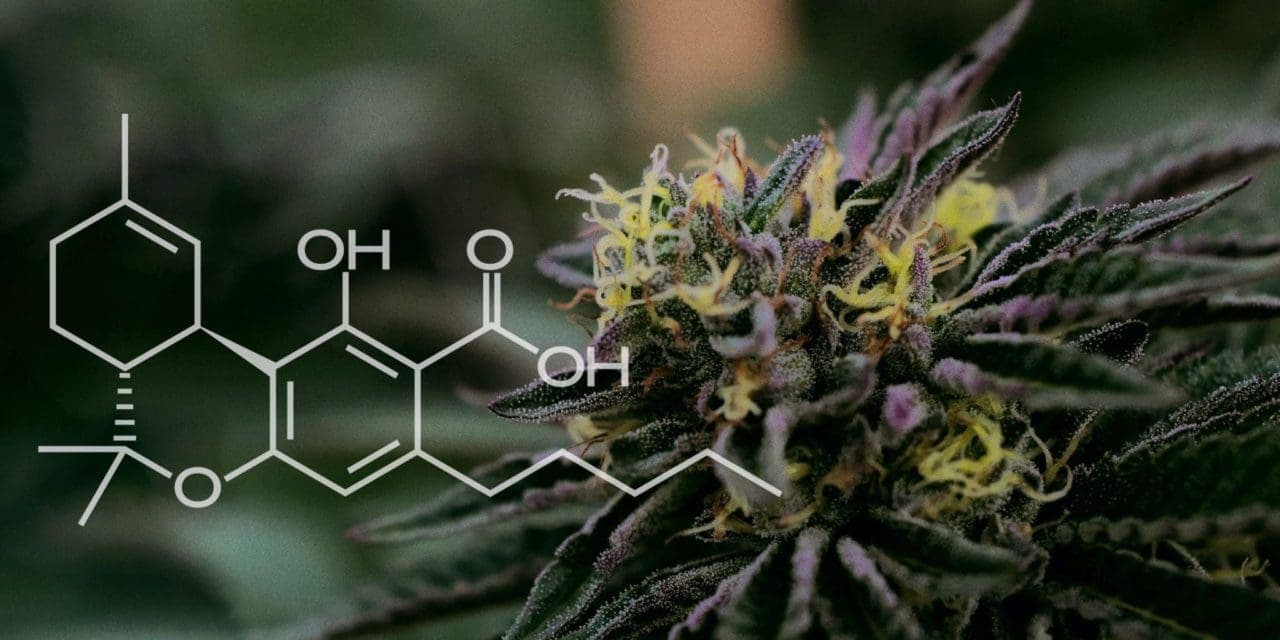
THC is short for tetrahydrocannabinol. It’s the main compound in cannabis, responsible for the intoxicating “high” you may feel when you consume some cannabis products.
In addition to its intoxicating effects, THC offers potential health benefits, which has led both researchers and patients to explore it as a treatment for certain conditions and symptoms.
Get your medical marijuana card
What is THC?
THC is a type of cannabis compound known as a cannabinoid. It’s the dominant compound in most cannabis plants, which means that it occurs in higher concentrations than any other compound.
When cannabis plants contain enough THC to cause intoxication, they are often referred to as “marijuana.” In modern days, smokable flower from these plants usually contains between 15% and 35% THC.
When cannabis plants contain no more than 0.3% THC, they’re legally classified as hemp.
How does THC work?
Cannabinoids like THC affect your body’s endocannabinoid system. This bodywide system helps regulate various processes, including:
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Mood
- Sleep
- Energy levels
- Brain functions, such as learning, focus, and memory
THC works by binding to receptors in your endocannabinoid system, leading to changes in your perception of pain, appetite, and other functions.
THC is intoxicating because it interacts with brain receptors in a way that can produce psychoactive effects. These effects include noticeable changes in perception, feelings, and consciousness, among others.
What is the difference between delta-8 and delta-9 THC?
Delta-9 THC is the main form of THC produced naturally in cannabis plants.
Delta-8 THC is another form of tetrahydrocannabinol in cannabis with a slightly different chemical structure.
Unlike delta-9 THC, delta-8 THC is only found in trace amounts in cannabis plants.
Delta-8 THC binds to certain cannabinoid receptors less effectively than delta-9 THC, meaning it may produce milder psychoactive effects. But more studies are needed to confirm this.
While delta-8 THC could offer some health benefits, research on its benefits is early and limited compared to delta-9 THC. Further, most delta-8 THC products sold in stores are unregulated, unlike cannabis sold in licensed dispensaries. Because of this, the quality and safety of delta-8 THC products can vary.
What is THCA?
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the precursor, or inactive form, of THC.
THCA is found in raw cannabis flower buds. When it is heated in a specific way, it turns into THC. This heating process, known as decarboxylation, can be achieved through smoking cannabis flower or applying heat in another way, like baking cannabis flower in the oven.
When left raw, THCA is not intoxicating.
Is THC legal?
The legality of THC varies according to both federal and state laws. In fact, the amount of THC in cannabis plants plays an important role in the legal status of both marijuana and hemp products.
The legal status of cannabis, from which THC is derived, varies between states.
Cannabis with more than 0.3% THC is illegal at the federal level. However, dozens of states have legalized medical and/or recreational cannabis use.
Hemp is legal at the federal level, meaning products made from hemp that contain 0.3% THC or less are also federally legal.
What is a high dose of THC?
Generally speaking, any amount over 10 milligrams (mg) of THC could be considered a high dose for someone who doesn’t use cannabis products frequently. Between 3 and 5 mg of THC is enough to cause intoxication in people who are new to using cannabis.
That said, there are no universal standards to determine what is a high or low dose.
What might be considered a high dose for one individual may be a low or moderate dose for another. That’s because factors like tolerance, frequency of use, and consumption method can all affect how strongly you feel the effects of THC.
Work with a cannabis-trained healthcare professional to determine the best dose of THC for your health needs.
What is a low dose of THC?
Most people are advised to start with 3 to 5 mg of THC or less. In most cases, this amount is low enough to prevent strong intoxicating effects.
If you’re using medical cannabis to manage a health condition, speak with your doctor before deciding on a starting dose. They may suggest a different amount based on your health needs.
Benefits and uses of THC
Studies show that THC may offer certain health benefits:
- Lowers inflammation: A review of studies reports that THC may help reduce inflammation. That said, most research in this area has been done in cells or animals, not humans.
- Eases pain: Research shows that THC may help manage chronic pain.
- Reduces nausea and vomiting: THC may help with nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy, according to a review of studies.
- Improves appetite: Studies show that THC can increase appetite.
- Supports positive mood: According to some animal studies, THC may have antidepressant effects, but more human studies are needed to confirm this benefit.
Prescription drugs that contain THC
Although cannabis is federally illegal, there are some prescription medications that contain a synthetic form of THC:
- Dronabinol: Prescribed to treat nausea, vomiting, and appetite loss in individuals undergoing treatment for cancer or HIV. The brand-name version, called Marinol, has been discontinued.
- Nabilone: Also prescribed to treat nausea, vomiting, and appetite loss in individuals undergoing treatment for cancer or HIV, nabilone is considered more potent than dronabinol. The brand-name version, called Cesamet, has been discontinued.
- Sativex (nabiximols): A medication that contains equal parts THC and CBD prescribed to help treat symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS).
Nabiximols is not currently available in the U.S.
Risks and side effects of THC
When used as directed, THC is generally well-tolerated by most individuals. That said, it can cause some side effects, especially if consumed in high doses.
Side effects of THC include:
- Dry mouth
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Impairment
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
Starting with a low dose of THC, like 3 to 5 mg or less, may help lower the risk of these side effects.
THC may also interact with certain medications. If you’re prescribed any medications, speak with your doctor before using THC.
In rare cases, heavy, long-term use of THC may lead to a condition called cannabis hyperemesis syndrome, which can cause severe and persistent vomiting.
Types of THC products
THC is found in several cannabis product types.
Cannabis flower
Cannabis flower is commonly smoked. It can also be vaporized or used to make edibles.
Amounts of THC vary between different cannabis strains. Most strains contain between 15% and 35% THC, although some contain as little as 1% THC.
Vaporizers
Cannabis vaporizers offer an alternative to smoking cannabis flower. Most vaporizers are handheld devices containing cannabis extracts, including THC.
Edibles
Cannabis edibles, such as gummies and baked goods, come in a variety of THC strengths.
Edibles may produce stronger effects than other methods of consumption because of how they’re metabolized in the body.
Tinctures
Cannabis tinctures contain extract that’s diluted in a carrier oil. They’re administered under the tongue, which allows THC and other cannabis compounds to absorb into the bloodstream quickly.
Topicals
Cannabis topicals are commonly used to provide localized relief to painful areas of the body.
The effects of THC in cannabis topicals stay localized, so they’re unlikely to cause intoxication, unless you use a transdermal patch.
How long does THC take to work?
It can take minutes or hours to feel the effects of THC. How long it takes THC to work depends on:
- Your dose: Higher doses of THC tend to take effect more quickly.
- The product type: Some products take effect more quickly than others because of how they are broken down and absorbed into your body. For example, vaporized products can take effect in 15 minutes or less, while edibles may take up to 2 hours to cause effects.
- Your unique traits: Some people’s bodies absorb THC more quickly than others because of differences in metabolism, tolerance, and other factors.
The bottom line: THC is an intoxicating cannabis compound that may offer some health benefits
THC is the main compound in cannabis. It’s responsible for the high you may feel after consuming cannabis.
Research shows that THC may offer certain health benefits, such as pain relief and anti-nausea effects.
If you want to use THC to help treat a symptom or condition, consider scheduling an appointment with Leafwell. A Leafwell healthcare provider can guide you on dosing and choosing the best product for your health needs.
Resources
- Antidepressant-like effect of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa L. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0091305710000730
- Cannabinoid regulation of acute and anticipatory nausea. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/can.2016.0006
- Cannabis for chronic pain: Challenges and considerations. https://accpjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/phar.2115
- Marijuana toxicity. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430823/
- Medical cannabis activity against inflammation: Active compounds and modes of action. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.908198/full
- Review of delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC): Comparative pharmacology with Δ9-THC. https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.15865
- Review on clinical studies with cannabis and cannabinoids 2010-2014. https://cannabis.maryland.gov/Documents/Article%20to%20be%20posted%20on%202-29-16.pdf
- Tasty THC: Promises and challenges of cannabis edibles. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5260817/
- Understanding THC concentration and potency. https://lcb.wa.gov/education/understanding_thc_concentration_and_potency
Get Your Medical Card
Frequently asked questions
Continue reading to learn more about THC.